NEW FOCUS MICROPLASTICS
Stop replenishment!
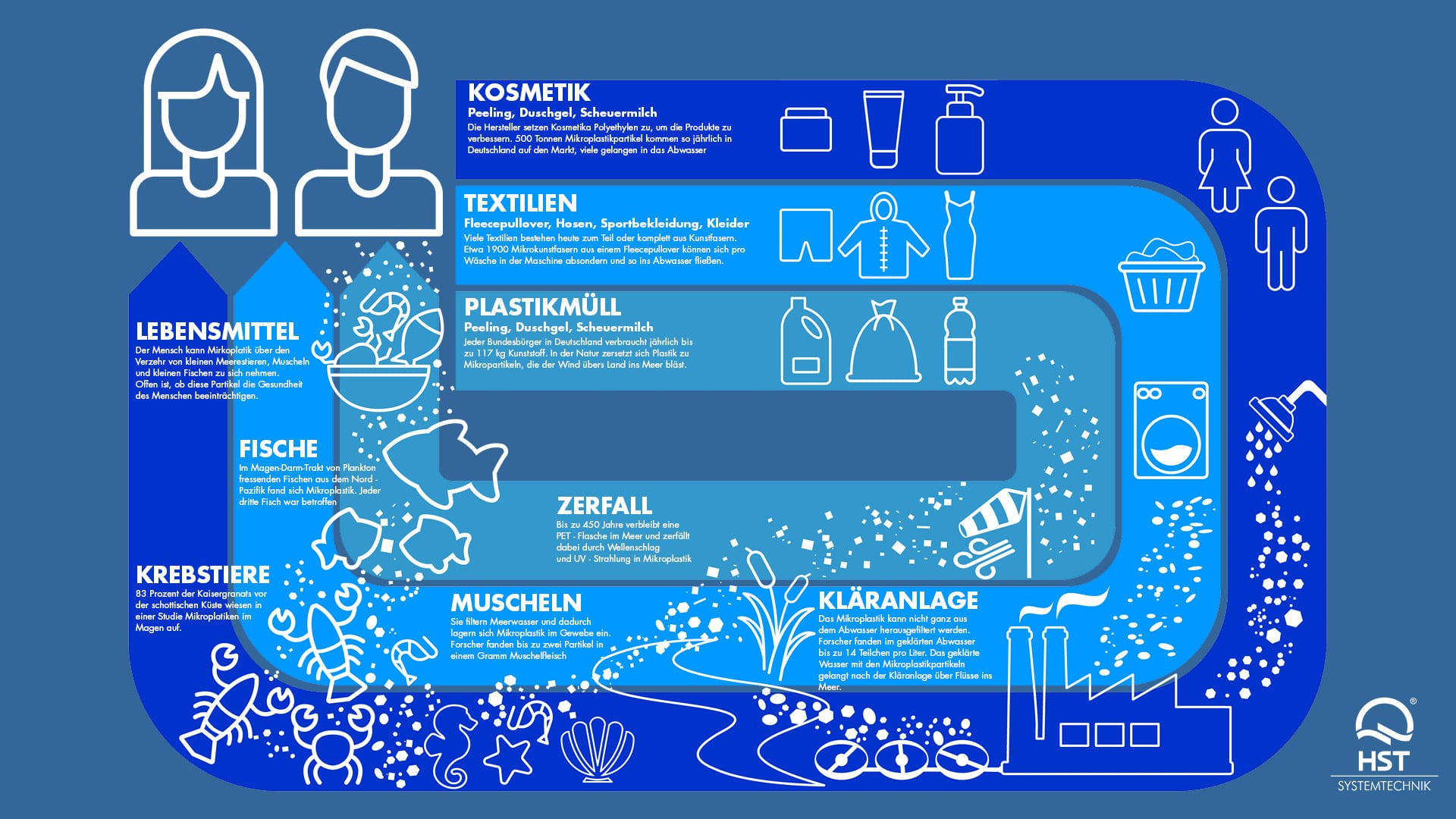
The topic of microplastic has been known since the 1970s and has been more or less shadowy. Today, microplastics is increasingly on everyone’s lips. Suddenly it comes back in the form of food from the sea back to the countries of origin. In the sea, the amount of plastic increases continuously. The five plastic islands in the oceans with macroplastic, the precursor to secondary microplastics, are growing permanently. The islands are now to be reduced media effective. But is that a substantial contribution? – Only 20% of plastic waste in the sea is floating on the surface, i. up to 30 meters below the water surface. 80% are – at present irretrievably – on the seabed. In Germany, macroplastic accounts for 26% of plastic emissions [from Frauenhofer UMSICHT]. The bulk is microplastic.
Five facts
- 74% of the emitted plastic is microplastic
- 22% of the waste water passes into our inland waters unpurified
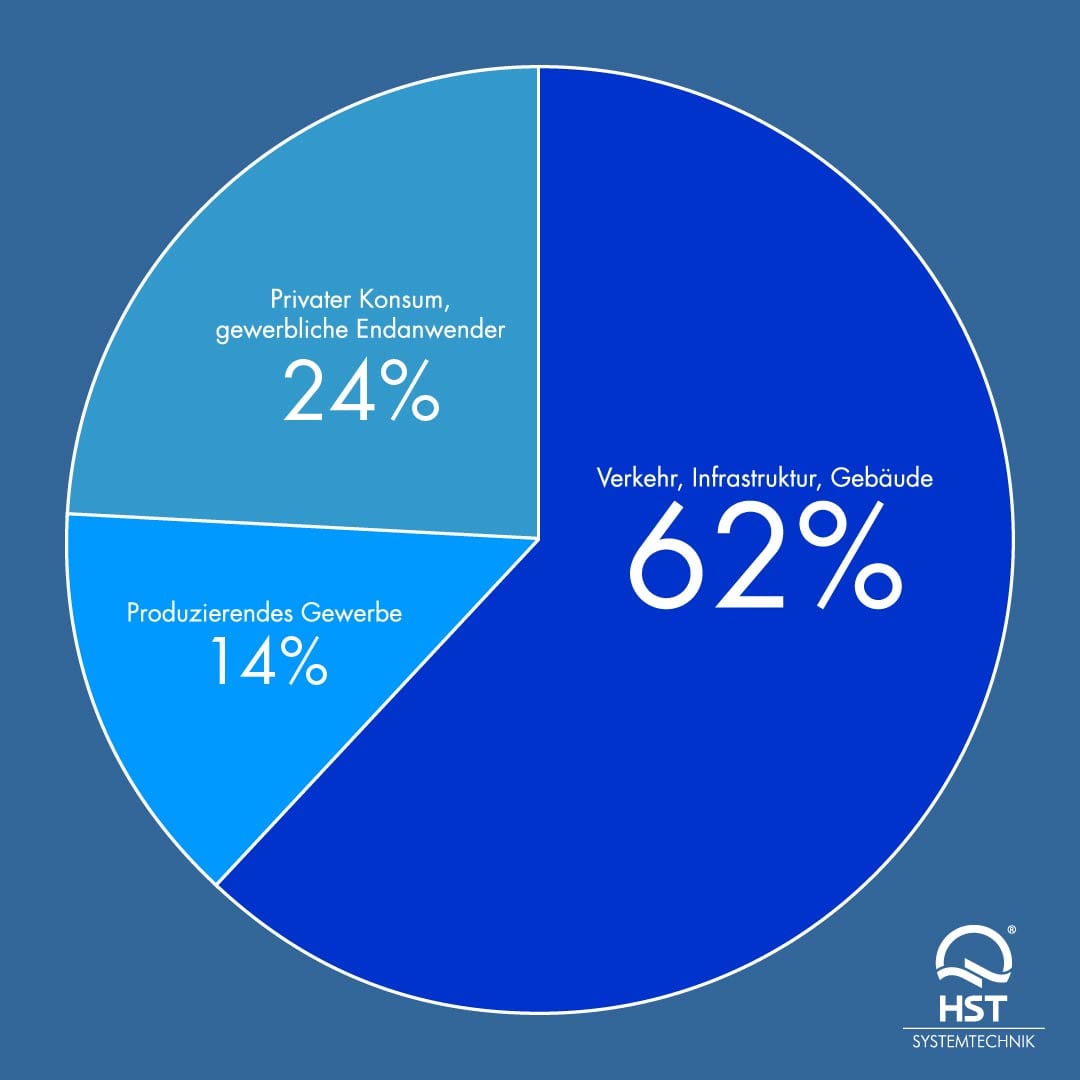
- Main causes: traffic, infrastructure, construction industry
- Inland and coastal waters significantly more polluted than offshore
- Intelligent channel management (machines and IT) reduces plastic emissions
Impact on human-beings
- Negative impacts on Fertility
- Deterioration of the immune system
- Increase in the mortality rate
The logical conclusion is that plastic emissions must be reduced. Fraunhofer Institute for Environmental, Safety and Energy Technology UMSICHT demands a reduction to a 27th. In the retail sector, initiatives are being taken to save plastic in order not to bring plastic to the market. The sewage treatment plants in Germany achieve a deposition of the microplastic by 95%, with 35% of the microplastic being applied again as sewage sludge.
In Germany, 22% of the wastewater (62% of the rainwater and less than 1% of the wastewater) is not treated in sewage treatment plants, but discharged into our inland waters unpurified. This happens at overflows in the sewer system as soon as they have to be relieved of an event such as heavy rain. At this critical point, the use of modern fine rakes is a must. Advanced operators are familiar with HST solutions for overflows or are already using them. According to the current state of knowledge, the combined sewage system with its 13% share of unexplained precipitation water is far more efficient in terms of plastic retention than the separation system with 43%. The concentration of particles / m3 is significantly higher in inland and coastal waters than in the high seas. Therefore, recovery in these areas is also particularly effective.
In less developed infrastructure regions, in addition to the micro- and the macroplastic, water flows unhindered. Here the importance of meaning shifts to macroplastic. This shift is compounded by the fact that in many countries there is no deposit and often no collection system. The result is rivers with a closed plastic layer.
HST Systemtechnik has long been committed to the reduction of plastic emissions. Initially, by assisting ocean-going projects such as Pacific Garbage Screening to dump the macro-plastic islands, HST is now shifting its focus, according to scientific evidence, to reducing the entry of microplastics from inland waters across rivers, harbors, and coastal waters. The plastic waste is thus cut off the supply.
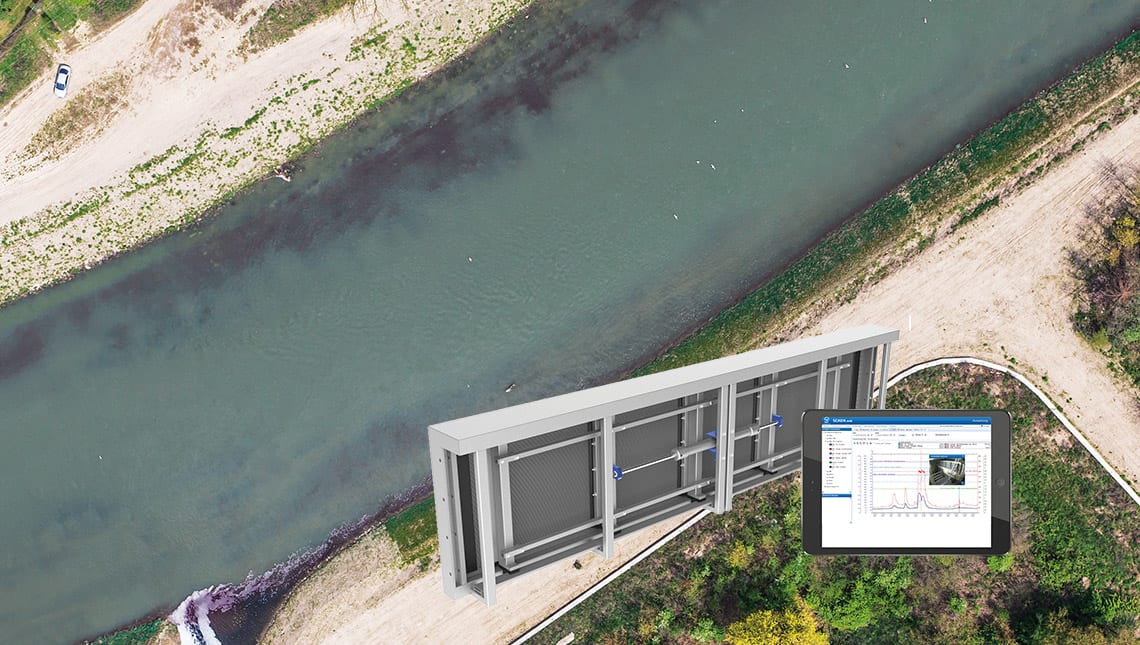
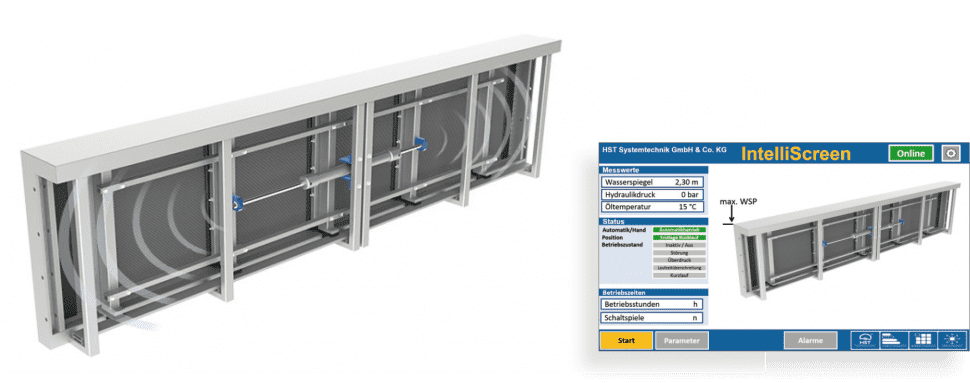
Even today, HST technology, with its digitized, intelligent rake and artificial intelligence, holds back a maximum of microplastics from the amounts of tee water. Based on the optimal control of the freight flows in the channel, the HST rake is only cleaned depending on the event. As a result, a filter cake accumulates in front of the rake, which retains not only macroplastic but also microplastics and other fines and suspended matter. This affects the 22% share of unpurified wastewater, making it an essential step in reducing plastic emissions.
Impact on the ecosystem
- Negative effect on organisms by strangulation
- Effects on organisms by ingestion and excretion (Egestion); through accumulation, translocation and transfer within the food chain
- Chemical hazards due to release of additives, monomers and critical metabolites
- Carryover of species (drifting)
- Physical effects on an ecosystem
To move further towards the reduced emissions target of 3.7%, new technologies are needed to stop microplastic replenishment from inland waters. To this end, HST initiates a university challenge among the brightest minds. In the autumn of 2019, a competition will be launched for the best solution for extracting plastic emissions from inland waters. The best solution will be included in the product portfolio by HST.
Everybody has to do his part so that the problem of plastic waste in waters does not increase any further and above all does not get lost in discussions. The share of urban water management is considerable. Where rakes are used today, the macroplastic can already be absorbed. A contribution against microplastics and other suspended and fines is so far only the HSR rake with IntelliScreen. The ecological Effizeinz is significantly increased by the use of an Intelli-led channel management and finds its current maximum efficiency through the inclusion of the precipitation portal Nira.web. This system technology by HST means that only a fraction of the microplastic, which is normally chipped off through thresholds, first reaches inland waters and then into oceans.


News on the topic

Prepared for the future – networking is the keyword
Luxembourg relies on HST’s innovative computer systems with IntelliScreen The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg is considered as exemplary in many respects in Europe. And this…

Water Management in China
Innovation and technology leadership secure long-term HST business in China. Water management in China faces major challenges when it comes to tackling the country’s massive…

Mode of action – IntelliScreen
A significant part of the precipitation is derived from sewage networks in towns and communities. Depending on the load and the drainage concept (mixing or…

Fronkreisch! Fronkreisch! Bonjour PARIS, voilà HST
In September 2018, we delivered and installed the first HST-Screening system for floating material restraint for the city Nanterre in district 92, Paris. It consists…

Smart Machines: From Steel to Chip
Intelli systems form the backbone of digital (r)evolution Automation technology, software and IT communication have constituted the basis of modern equipment systems in municipal infrastructures…
Definitions Plastic types and fractions
(Fraunhofer – BMU)
See BMU 2015 p. 10f – does not differentiate between type A and type B
Classification and designation of plastic waste
Classification and designation of plastic waste in the sea on the basis of their size compared to typical dimensions of affected animals and industrial applications of. Plastic (Source: own illustration after JRC 2013, STAP 2011)
References:
- Bertling, Jürgen; Bertling, Ralf; Hamann, Leandra: Plastics in the environment: micro- and macro-plastic. Causes, quantities, environmental fates, effects, solutions, recommendations. Short version of the consortium study, Fraunhofer Institute for Environmental, Safety and Energy Technology UMSICHT (ed.), Oberhausen, June 2018
- Helcom: Blastic – plastic pathways from land to sea. Pressure 3-2015.
- Essel, Roland; Angel, Linda; Carus, Michael: Federal Environment Agency: Sources of microplastics relevant to marine conservation in Germany. 63/2015.
- Federal Environmental Agency: microplastic in the sea – how much? From where? Press release 34, 2015.
- Federal Environmental Agency: Together against the littering of the seas. , 2014.